
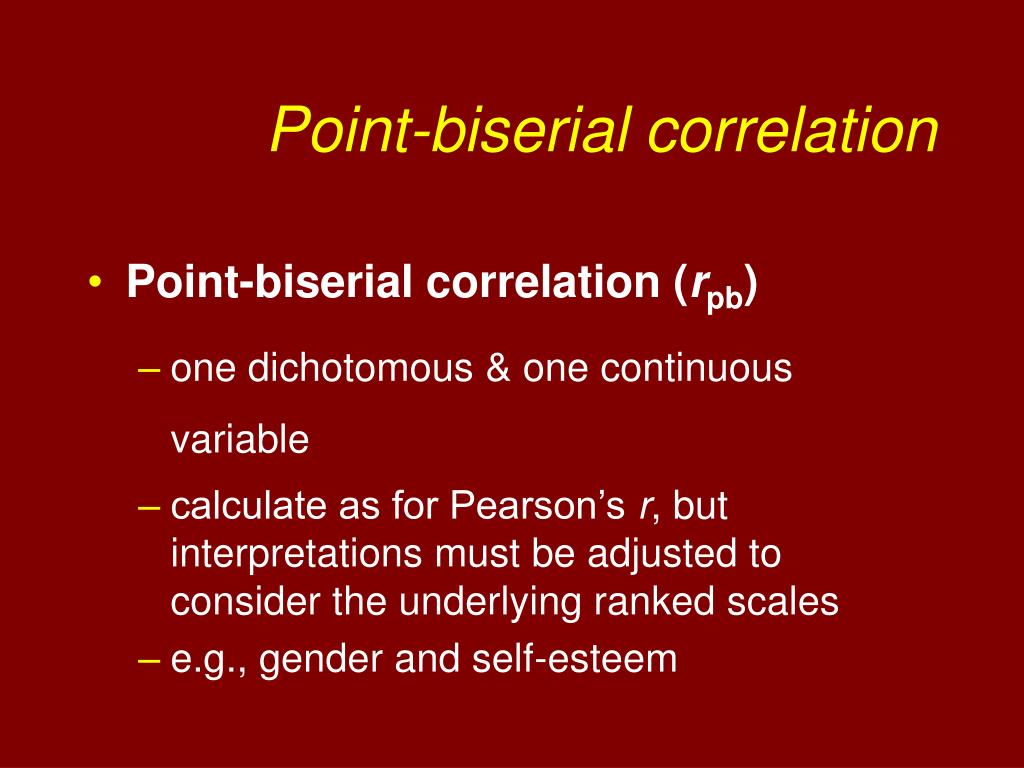
Hence, the point biserial correlation coefficient is the one you should go for in case you are interested in studying the relationship between a nominal and a numerical feature. So intrinsically, the two variables are treated by the Pearson correlation coefficient as quantitative, although one of them is qualitative. The only reason that you get a similar value is the fact that the nominal categories are represented as numbers, and numbers, in general, are supposed to be quantitative. Although it can pick noodles up, is it really the right tool for the task? On a similar note, the Pearson correlation coefficient assumes that each dataset is normally distributed, which is invalid for a categorical variable. Point-Biserial and Biserial Correlations The point-biserial correlation is a special case of the product-moment correlation in which one variable is continuous and the other variable is binary (dichotomous). Have you ever tried eating noodles with a spoon, a job that is fit for a fork?Ī spoon assumes that you will use it for having a soup, a custard, ice cream, or something of that texture. Answer: They are somewhat different here are the definitions. ) So why would one want to use another measure when the Pearson Correlation Coefficient does the job? (In case you are interested in the proof, read this thread. Now, the point biserial correlation coefficient turns out to be a special case of the Pearson correlation and comes out to be equivalent to it. But what happens when one of the variables is not numeric but an attribute and we want to look at the correlation between a numeric variable and the attribute. The point biserial correlation coefficient lies in the range and its interpretation is very similar to Pearson’s Product Moment Correlation Coefficient, i.e., stronger higher the value of the point biserial correlation coefficient, stronger is the relationship between the two variables (one qualitative and one quantitative), and vice versa. Answer: The correlation coefficient is calculated when both the variables under consideration are numeric variables. 0 corresponds to no association (the means of the quantitative variable for the two categories of the qualitative variable are identical).Formula for Point Biserial Correlation Coefficient What do you mean by biserial correlation? The biserial correlation is a correlation between on one hand, one or more quantitative variables, and on the other hand one or more binary variables.

Both covariance and correlation have distinctive types. Covariance is a measurement of strength or weakness of correlation between two or more sets of random variables, while correlation serves as a scaled version of a covariance. Let’s look at an example of two variables cohering. Coherence means how much the two variables covary. In this concept, both variables can change in the same way without indicating any relationship. Point biserial correlation is an estimate of the coherence between two variables, one of which is dichotomous and one of which is continuous. Is covariance and correlation the same thing? If all the researchers give similar ratings, the test has high interrater reliability. Then you calculate the correlation between their different sets of results. To measure interrater reliability, different researchers conduct the same measurement or observation on the same sample. How do you measure inter item reliability? It is expected that if a participant gets a question correct they should, in general, have higher overall assessment scores than participants who get a question wrong. The item total correlation is a correlation between the question score (e.g., 0 or 1 for multiple choice) and the overall assessment score (e.g., 67%). What does a high item-total correlation mean? How do you find inter-item correlation in SPSS? How do you interpret item-total correlation? Click Continue and then OK to generate the output. In the inter-item box, select Correlation.
In the box description, select Item, Scale, and Scale if item deleted. In order to run an a priori sample size calculation for a point biserial correlation, researchers will need to seek out evidence that provides the proposed. How do you do inter-item correlation in SPSS? values 0.4 and above indicate very good discrimination.values between 0.2 and 0.39 indicate good discrimination.values between 0 and 0.19 may indicate that the question is not discriminating well.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
